A paper exploring the combination of Oxygen Enhancement Ratio and Relative biological effectiveness in proton therapy treatment planning. First author Helge Henjum (helge.henjum@uib.no) is Post Doc. in the Bioproton project.
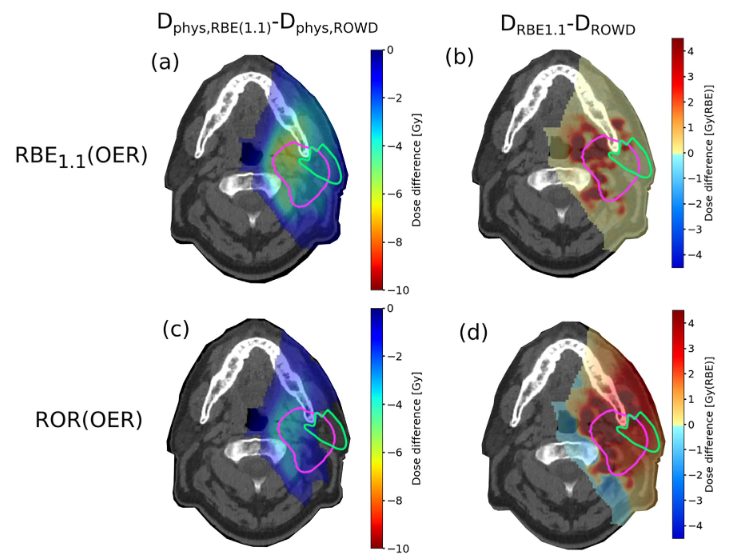
The effect of protons in hypoxic cells is a topic of high clinical relevance as hypoxia is related to poor treatment outcome. A combined RBE and OER weighted dose (ROWD) calculation method was implemented in a FLUKA Monte Carlo (MC) based treatment planning tool. The method is based on the linear quadratic model, with α and β parameters as a function of the OER, and therefore a function of the linear energy transfer (LET) and partial oxygen pressure (pO2). Proton therapy plans for two head and neck cancer (HNC) patients were optimized with pO2 estimated from [18F]-EF5 positron emission tomography (PET) images. For the ROWD calculations, an RBE of 1.1 (RBE1.1,OER) and two variable RBE models, Rørvik (ROR) and McNamara (MCN), were used, alongside a reference plan without incorporation of OER (RBE1.1).
The FLUKA MC based tool was able to optimize proton treatment plans taking the tumor pO2 distribution from hypoxia PET images into account. Independent of RBE-model, both elevated LET and physical dose were found in the hypoxic regions, which shows the potential to increase the tumor control compared to a conventional optimization approach.
Leave a comment